
Around 70% of the waste in water sinks to the bottom of the ocean or decomposes into micro and nanoplastics, amounting to tens of millions of tons. So the European Horizon Maelstrom research project put together an international research team, including representatives from Tecnalia in Spain, and developed the Robotic Seabed Cleaning Platform. Its core component is an underwater robot equipped with a gripper and a suction device that moves flexibly in six degrees of freedom with the help of eight winches.
Using sensors and cameras, the robot detects trash, automatically positions itself above it, and lifts objects weighing up to 130 kg − including bicycles, tyres, boxes and nets. Smaller parts or plastic pieces floating in the water are recovered by suction. “Since we operate from the surface and activate grabs or suction cups only when needed, we achieve high selectivity, minimising the impact on the seabed ecosystem,” explains Mariola Rodríguez, project manager of Maelstrom at Tecnalia.
The positioning winches are synchronously controlled by AX5118 servo drives and AM8071 servomotors from Beckhoff. “To ensure robust, accurate, positioning, we chose brushless synchronous servomotors,” says Jose Gorrotxategi, the electronics engineer on Tecnalia’s cable robotics team. The steel cables of the winches allow the robot frame to be positioned precisely underwater and held in place with high stability, despite the strong currents. Encoders on the motor shafts detect the angular position and revolutions of the cable drums, which indirectly allows them to establish the length of the coiled cable. Electromagnetic brakes and monitoring of cable tensions by means of force sensors ensure the required safety. For control and monitoring purposes, the frame of the underwater cable robot contains a number of sensors and cameras for manual, automatic and remote operation. “The cameras and lights allow manual control,” explains Pierre-Elie Herve, the mechanical and control engineer on Tecnalia’s cable robotics team.
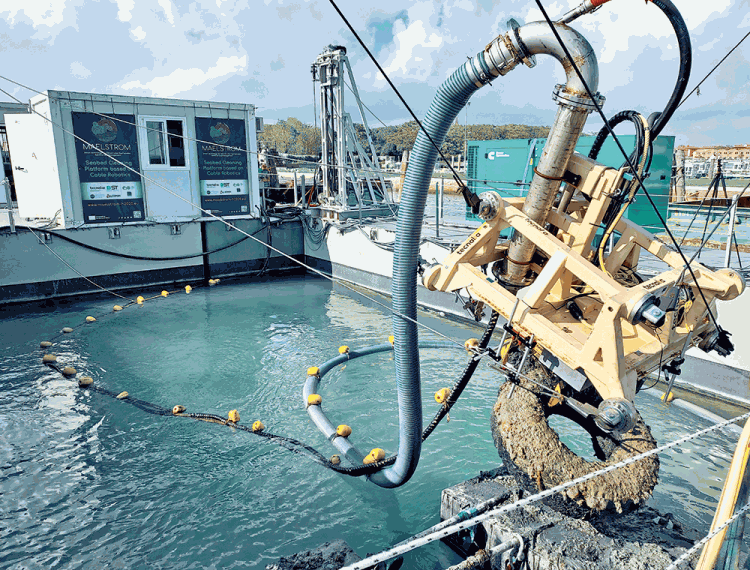
The operator can click on interesting locations on the seabed in the camera image, which the robot then approaches autonomously. A pressure sensor on the robot frame detects the diving depth, and an inertial measurement unit regulates its position in the water. The distance of the mobile platform to the seabed, and its relative velocity to it, is recorded by a doppler velocity log via four sonar sensors.
Other sensors are located on the pontoon at the water surface, including a pressure sensor to compensate for atmospheric pressure changes during depth control. Two real-time kinematic GPS units determine the position and vertical orientation of the barge in real time. All data from these different systems is incorporated into the control and position regulation of the robot. Based on these values, the robotic platform can perform tasks such as precisely approaching and holding the positions previously selected on depth maps. “This ability has proven to be a key feature in the very turbid waters of the Venetian Lagoon,” says Rodríguez.
With its total of twelve axes – eight winches and four vertically movable slides on the pontoon masts – the underwater cable robot is controlled by TwinCAT 3, installed on a C6650 control cabinet industrial PC. In addition to the cable force monitoring, several emergency stop buttons along the system ensure safe operation.
A further four distribution boxes, mounted decentrally on the cable winches, contain the I/O interface modules and the electronics for cable force measurement. The connection between the control cabinet and the distribution boxes is established via Ethercat P. This extension of the EtherCAT technology makes it possible to transmit both the DC supply and the EtherCAT real-time communication in a single cable.
When controlling the cable robot by joystick, the operator uses the estimated position of the mobile underwater platform and the cameras located on the mobile platform. Using the HMI, the operator can select the various control modes and monitor all functions based on the sensor values, in addition to visual control via underwater cameras.
The camera system for underwater perception mainly enables visual servo. In addition to manual operation, the rack can also autonomously identify, target and collect trash. This works on the basis of artificial intelligence, which is able to identify the marine debris and select the most appropriate removal device.
The software developed for the robotic platform for cleaning the seabed calculates in real time the geographic position of the robot thanks to real-time GPS devices that measure and report the position or orientation, and simultaneously monitor and control the winches. In addition, the position of the robot is displayed on the map of the seabed, which also shows the position of the waste.
| Tel: | +27 11 795 2898 |
| Fax: | 086 603 6868 |
| Email: | [email protected] |
| www: | www.beckhoff.com |
| Articles: | More information and articles about Beckhoff Automation |

© Technews Publishing (Pty) Ltd | All Rights Reserved